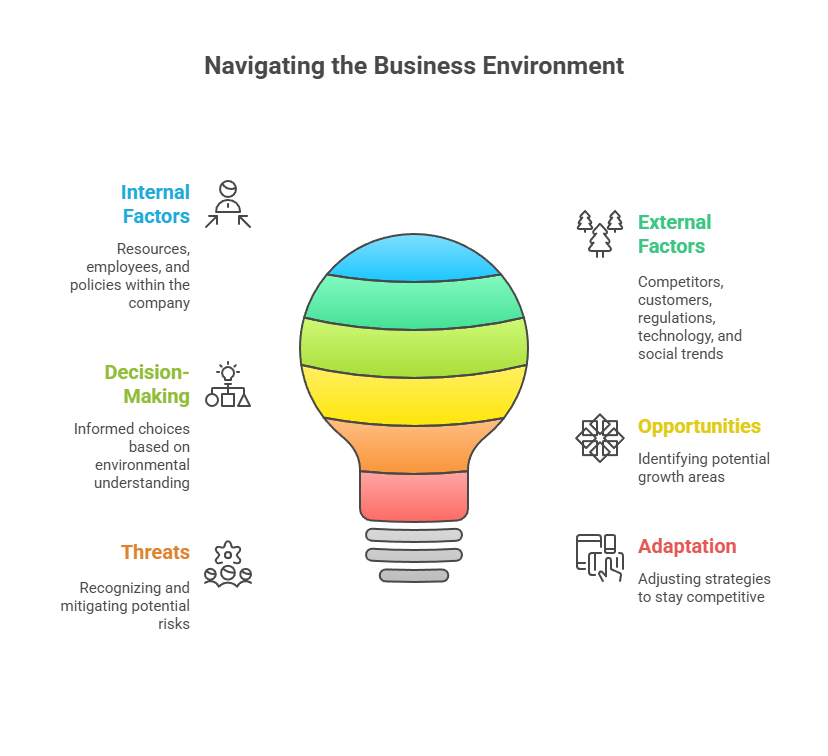
1. Definition & Importance of the Business Environment
The business environment refers to all the internal and external factors that influence a company’s operations, decisions, and performance. These include the company’s resources, employees, policies, competitors, customers, government regulations, technology, and social trends. A well-understood business environment helps leaders make informed decisions, identify opportunities, and avoid potential threats.
In practical terms, if you run a small café, your business environment includes things like your suppliers, customer preferences, competing cafés nearby, food safety laws, and even the weather (affecting foot traffic). By understanding these factors, you can adjust your menu, pricing, or marketing strategy to stay competitive.
In a fast-changing world, companies that continuously monitor and adapt to their environment are better equipped to survive and grow. For learners, the key takeaway is: the environment is not static—it shifts with economic trends, technology changes, and consumer behaviours. Your ability to read and respond to these shifts is a core business skill.
2. Internal vs. External Environment
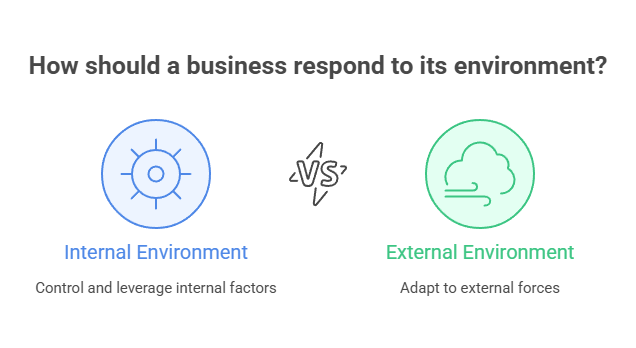
The internal environment consists of factors within the organization’s control—its structure, employees, company culture, operational processes, and resources. For example, if a retail store trains its staff well, maintains a positive culture, and invests in efficient inventory systems, these internal strengths help it perform better.
The external environment, on the other hand, includes factors outside the company’s direct control, such as economic trends, technological advancements, legal regulations, and social preferences. While a business can’t change these forces, it can respond strategically. For instance, if a new tax law increases costs, a company might adjust pricing or find cost-saving measures.
The distinction is critical: internal factors are levers you can pull directly, while external factors require adaptation. Successful businesses align their internal strengths to meet external challenges. When evaluating a situation, always ask: “Is this something we can change, or something we must adapt to?”—this mindset improves strategic decision-making.
3. Key Environmental Forces: The PESTLE Framework
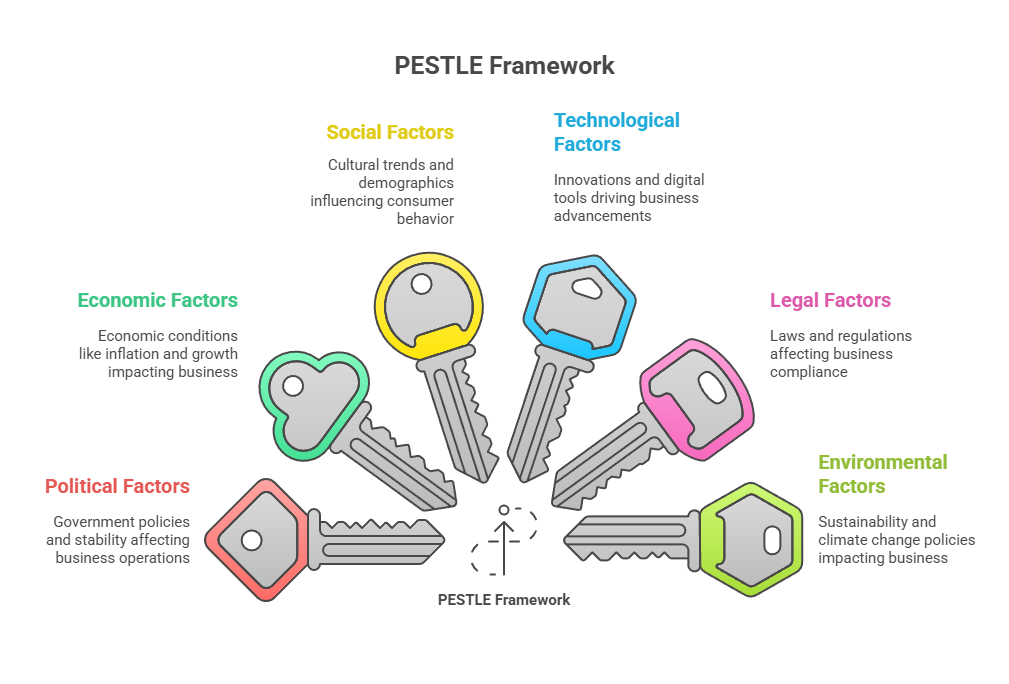
The PESTLE framework is a tool for analyzing the macro-environmental forces affecting a business:
Political: Government policies, stability, trade laws.
Economic: Inflation, interest rates, unemployment, economic growth.
Social: Cultural trends, demographics, consumer lifestyles.
Technological: Innovations, automation, digital tools.
Legal: Laws and regulations affecting operations.
Environmental: Sustainability, climate change, environmental policies.
For example, a smartphone company might face technological pressure to release new features faster, social demand for eco-friendly products, and legal requirements for data privacy.
Applying PESTLE helps businesses spot opportunities (e.g., a favorable trade agreement opening new markets) and threats (e.g., stricter environmental laws increasing production costs).
For you as a learner, this framework is like a “business weather forecast”—it won’t predict everything, but it helps you prepare for the big forces that could impact success.
4. Activity: Identify External Factors Affecting a Well-Known Company Today
Instructions:
Choose a company you are familiar with—such as Apple, Tesla, Starbucks, or a local business. List at least three external factors currently impacting it using the PESTLE framework. For each factor, write one sentence explaining the potential impact.
Example with Starbucks:
Economic: Rising coffee bean prices increase production costs.
Social: Growing demand for plant-based milk leads to menu expansion.
Environmental: Pressure to reduce single-use plastics drives packaging changes.
This exercise helps you connect theory to real-world examples, sharpening your ability to scan the environment and think strategically—exactly what managers and business owners do when planning.